Check whether cluster communication is abnormal
This article introduces the troubleshooting ideas for abnormal communication between the Rainbond console and the cluster.
The cluster communication is abnormal or the cluster end loses response
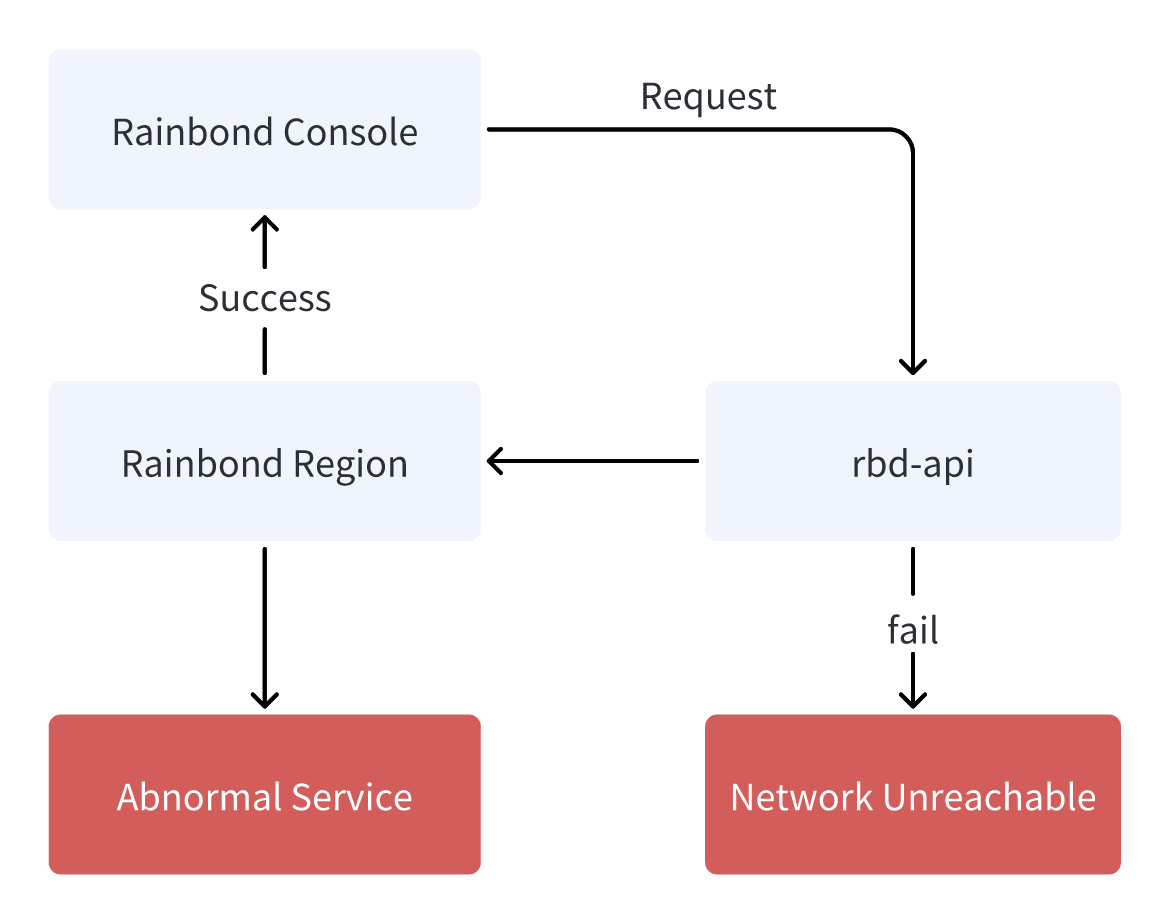
Rainbond is divided into two layers, the console and the cluster. The console communicates with the cluster through the API. If the communication between the console and the cluster is abnormal, the console cannot be used normally.
There may be the following reasons for the exception:
- The network between the console and the cluster is disconnected.
- The API service on the cluster side is unavailable.
- The API service on the cluster side is blocked by the firewall.
Troubleshoot ideas
If such problems occur, you can troubleshoot according to the following troubleshooting ideas.
Check the network between the console and the cluster
First, check the log of the console, go to Platform Management -> Log -> Console Log of the console, if https://192.168.1.1:8443 time out appears, it means that the console and the cluster end network issue.
You can enter the terminal of the console and use the ping command to check whether the network between the console and the cluster is smooth.
If the network is disconnected, you can check whether the console and the cluster network are in the same network segment. If not, you can configure the routing table for network communication.
Check cluster-side API services
If the network between the console and the cluster side is smooth, and the 8443 port is smooth, you can check whether the API service on the cluster side is normal.
Use the following command to check whether the API service is normal:
kubectl get pod -l name=rbd-api -n rbd-system
If the API is abnormal, you can view the logs of the API service through the following command:
kubectl logs -fl name=rbd-api -n rbd-system
Check according to the error information in the log.
Or try restarting the API service:
kubectl delete pod -l name=rbd-api -n rbd-system
Check console and cluster ports
If the network between the console and the cluster is smooth and the API service is normal, you can check whether the ports 8443 on the console and the cluster are unblocked. Use the telnet command to check whether the port 8443 on the console and the cluster side is unblocked.
If it fails, you can check whether the 8443 port on the cluster side is blocked by the firewall. If it is blocked by the firewall, you can configure the firewall rules for port communication.
common problem
remote error: tls: error decrypting message
Viewing the log of the rbd-api service shows the following error:
http: TLS handshake error from 10.42.0.1:35590: remote error: tls: error decrypting message
The reason for this error is that the certificate of the API service on the cluster side is inconsistent with that of the console, which makes the console unable to communicate with the API service on the cluster side.
You can view the cluster connection information through the grctl config command.
$ grctl config
apiAddress: https://47.104.161.96:8443
ca.pem: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
xxxxx
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
client.key.pem: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
xxxxx
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
client.pem: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
xxxxxx
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Copy the printed content to Platform Management -> Cluster -> Edit in the console, and click Save.
- apiAddress corresponds to API address
- ca.pem corresponds to API-CA certificate
- client.pem corresponds to API-Client certificate
- client.key.pem corresponds to API-Client certificate key
There cannot be spaces on the left and right sides of the certificate, otherwise the certificate will not be recognized.
If it is determined that the certificate of the console is consistent with the certificate of the cluster, but the problem still occurs, you can try to regenerate the certificate of the cluster.
# Delete the certificate on the cluster side
kubectl delete secret rbd-api-client-cert rbd-api-server-cert -n rbd-system
# Restart the operator to regenerate the cluster-side certificate
kubectl delete pod -l release=rainbond-operator -n rbd-system
# Restart the api service
kubectl delete pod -l name=rbd-api -n rbd-system
After the operator is restarted, the cluster-side certificate will be regenerated, and the cluster information can be obtained through grctl config again and copied to the cluster console.